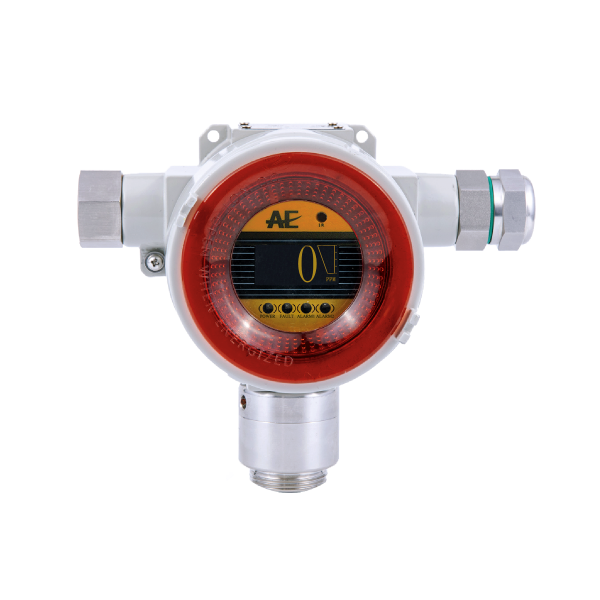
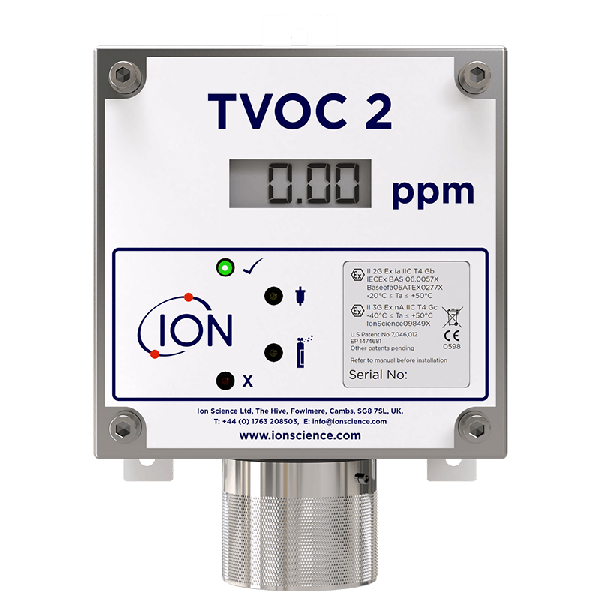
VOC Gas Detection
Volatile organic compounds, or more commonly known as VOCs are gases that are emitted into the air from products such as common household materials and products including paints, cleaning products or processes found in many industrial and commercial activities such as combustion processes.
Common VOCs include benzene, ethylene glycol, acetone, formaldehyde, methylene chloride, tetrachloroethylene, toluene, xylene, and 1,3-butadiene.
VOCs not only differ based on the boiling point of each chemical, but they also differ on the health effects when breathed in. While some VOCs are not known to cause any short or long term health effects, others are known to be highly toxic and can cause a range of adverse health effects including difficulty breathing, nausea, damage to the nervous system and even cancer. The time taken for the removal of volatile organic compounds from polluted air can differ for every compound. As it takes a long time for VOCs to dissipate it is best to use a PID detector to monitor and screen VOCs for immediate feedback on the worker’s environment.
The monitoring of VOC emissions with fixed photoionisation detectors is not only important for the protection of personnel on-site but is also important for the prevention of adverse environmental impacts on the local, regional, and global atmosphere due to its ability to react with other gases.
Volatile Organic Compounds Monitoring Equipment
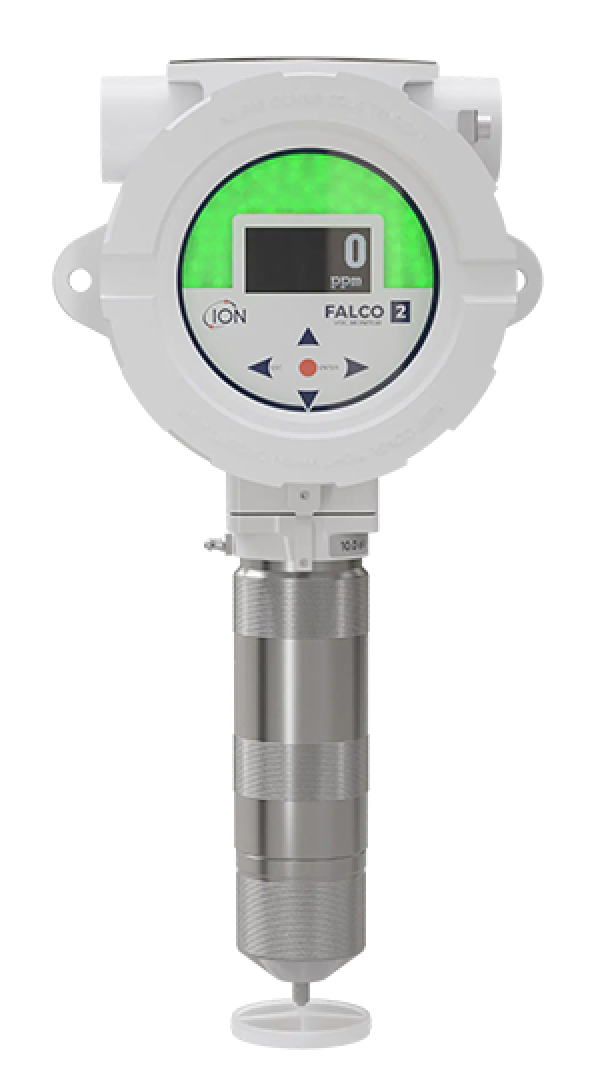
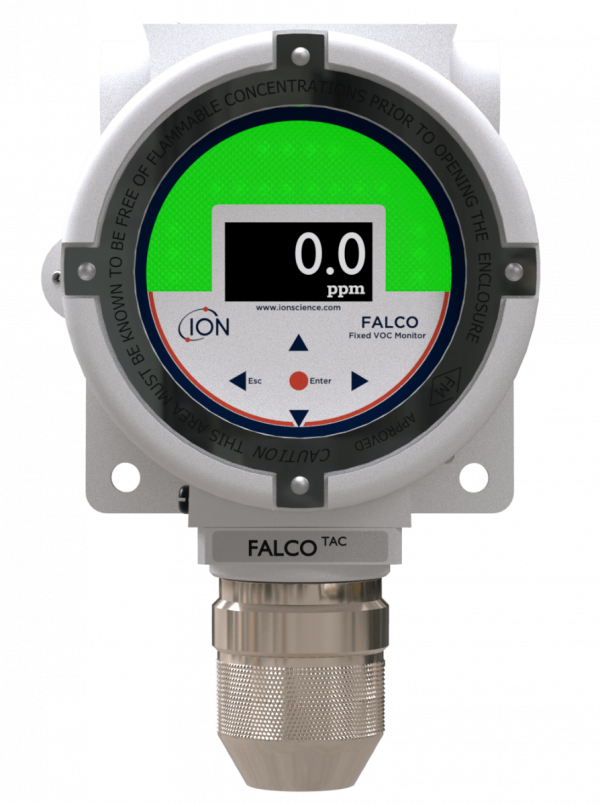
Air-Met Scientific offers the latest in fixed photoionisation detectors for the continuous and accurate detection of volatile organic compounds. Selecting the correct VOC detector is key for ensuring a safe workplace and site. When selecting the right fixed photoionisation detector (PID) for stationary applications, there are several key features that users typically consider. Here are some important features to look for in fixed PIDs:
Gas Detection Range:
The detection range refers to the concentration levels of gases or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that the PID can accurately detect. It is crucial to choose a fixed PID that covers the desired range of substances you need to monitor in your specific environment.
Sensitivity:
Sensitivity is a measure of the PID's ability to detect low concentrations of gases or VOCs. Higher sensitivity allows for the detection of trace amounts of hazardous substances. The sensitivity requirement depends on the specific application and the minimum concentration levels of concern.
Response Time:
The response time indicates how quickly the PID can detect and display changes in gas or VOC concentrations. Faster response times are essential for real-time monitoring, enabling prompt action in case of sudden increases in hazardous levels.
Accuracy and Precision:
Accuracy refers to how closely the PID's measurements align with the true gas concentrations, while precision refers to the repeatability of the measurements. Reliable and precise PID measurements are crucial for ensuring the safety of workers and accurate assessment of environmental conditions.
Selectivity:
Selectivity refers to a PID's ability to differentiate between different gases or VOCs. Fixed PIDs such as the Titan Fixed Benzene Detectors are designed for specific compounds, while others such as the TVOC 2 Fixed VOC Detector are more versatile and able to detect a broader range of substances.
Communication and Integration:
Fixed PIDs often require integration into a larger monitoring or control system. Therefore, it is essential to consider the communication capabilities of the PID, such as analogue outputs (e.g., 4-20 mA) or digital protocols (e.g., Modbus), to ensure compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
Data Logging and Storage:
Fixed PIDs with data logging capabilities can record and store measurements over time, providing a valuable dataset for analysis, compliance reporting, and trend monitoring.
Environmental Considerations:
Consider the environmental conditions in which the fixed PID will be installed. Look for PIDs with appropriate protection ratings (e.g., IP ratings) to withstand dust, moisture, and temperature variations. Additionally, consider technology such as the Ion Science’s revolutionary typhoon technology which is capable of safeguarding the PID sensors from condensing moisture.
Maintenance and Serviceability:
Evaluate the ease of maintenance and serviceability of the fixed PID. Experienced service technicians at Air-Met Scientific can assist with the servicing and calibration of VOC fixed gas detectors.
Whether you require continuous VOC or benzene monitoring for petrochemical environments or monitoring within manufacturing plants, Air-Met Scientific offers a range of fixed photoionisation detectors from industry leaders designed to suit your needs.
Contact our team at one of our six locations across Australia today.