|
Term
|
Definition
|
|
Electromagnetic Field (EMF)
|
Electromagnetic fields or EMFs are invisible areas of energy (radiation) caused by the motion of an electric charge. Electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields exist wherever voltages and currents are present. We are surrounded by electromagnetic radiation everywhere in our environment, but it is invisible to the human eye.
In the case of high-voltage power lines, radiation is an undesired by-product whereas in the telecommunication industry radiation is exploited purposefully to transmit information. Electromagnetic fields have certain biological effects that can be detrimental to human health which is why every country has a governing body that places standards, regulations around the limits of exposure, and recommendations to protect workers and the general public. In Australia, the governing body for radiation protection and nuclear safety is the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA) and International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP)
|
|
Electromagnetic radiation
|
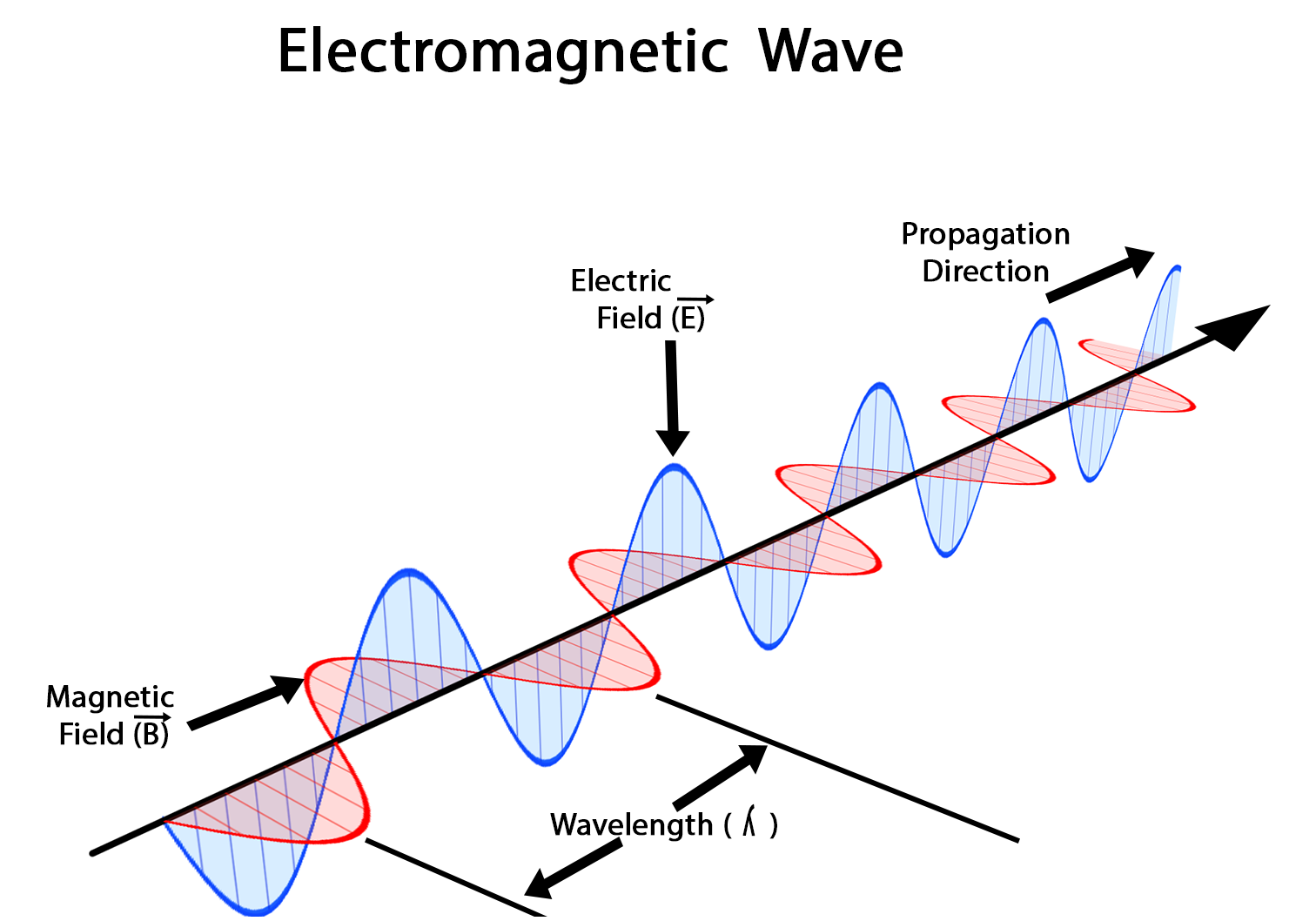
Electromagnetic radiation consists of the E field (electric field) which varies in magnitude in a direction perpendicular to the direction in which the radiation is travelling and the M field (magnetic field), oriented at right angles to the electrical field. This forms the electromagnetic wave. Electromagnetic radiation does not contain mass or charge. It travels in packets of radiant energy called photons or quanta.
|
|
Electromagnetic spectrum
|
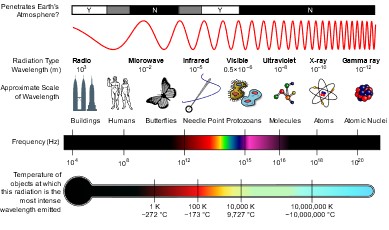
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of wavelengths and photon energies of all known types of electromagnetic radiation.
It covers frequencies from below one hertz to above 1025 hertz. The frequency range is divided in separate bands and the electromagnetic waves within each frequency begin at the low frequency (long wavelength) to high frequency (short wavelength).
|
|
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
|
Electromagnetic compatibility relates to the electromagnetic compatibility of an equipment. EMC guidelines defines how much radiation an equipment is allowed to emit and what amount of electromagnetic radiation it needs to withstand without causing electromagnetic interference with other equipment in its vicinity.
|
|
E field
|
The Electric field is the force generated around particles that bear electrical charge. This is measured in in units of volt per metre (Vm-1).
|
|
H field
|
Magnetic fields or H field is place near a magnet or an electric current where a physical field is created from a moving electrical charge that creates force on another electric charge. The magnetic field is measured in units of amperes per meter (Am-1).
|
|
Area radiation monitoring
|
Area radiation monitoring is vital to protect people who work within the vicinity of equipment that emits electromagnetic radiation. Area radiation monitors are used wherever there is a need for continuous or long-term EMF (Electromagnetic Field) observations and assessments. Narda’s range of EMF monitors for area radiation monitoring is equipped with reliable and accurate sensors and is ideal for long-term outdoor installations.
Area Radiation Monitors |
|
Personal Radiation Monitoring
|
Non-ionising radiation can pose a considerable threat to those exposed prolonged periods or where exposures exceed safe limits of exposure. Workers in industries such as telecommunications, radar antennas, welding or smelting are prone to a higher risk of radiation exposure. If adequate safety measures are not implemented, exposure to non-ionising radiation can leads to cataracts, buns to body tissue and increased risk of cancer.
Narda STS is a leading provider of personal radiation monitors such as the Narda Radman 2 and S3 Monitor.
Personal Radiation Monitors |
|
ELF Electromagnetic Fields
|
ELF or Extremely Low Frequency electric and magnetic fields exist wherever electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed in power lines or cables or used in electrical appliances. ELF occupies the lower end of the electromagnetic spectrum in the frequency range of 0-30Hz.
Acute exposure to ELF-EMF at high levels is known to affect the nervous system and muscle cells. High levels of ELF EMF are rare, but it should be constantly monitored for the safety of the general public. Workers in the electrical supply industry can be exposed to up to 2000 µT and electric fields up to 30 kV/m.
Low Frequency Radiation Meters |
|
High-Frequency Radiation
|
High-Frequency Electromagnetic frequency range between 100Khz to 300GHz. High-Frequency electromagnetic fields are radiated by an antenna in most cases, and it is primarily used in modern communications such as radio, television and cellular phones.
Electromagnetic fields are known to be detrimental to human health as an overexposure to high-frequency fields can cause burns and tissue damage in humans.
Workers employed in industries such as telecommunication, building and construction and emergency services can be exposed to risks of working near Radio Frequency (RF) sources. Narda STS has a range of EMF monitoring equipment designed to ensure occupational radiation safety and comply with the relevant governing regulations.
High-Frequency Meters |
|
Exposure Standards in Australia
|
|
Standard for Limiting Exposure to Radiofrequency Fields 100kHz to 300Ghz
|
This Standard for Limiting Exposure to Radiofrequency Fields – 100 kHz to 300 GHz by ARPANSA sets limits for human exposure to radiofrequency (RF) electromagnetic fields in the frequency range 100 kHz to 300 GHz. The Standard includes:
- Mandatory basic restrictions for both occupational and general public exposure involve all or part of the human body.
- Corresponding reference levels for measurable quantities derived from the basic restrictions.
- Approaches for verification of compliance with the Standard.
- Requirements for management of risk in occupational exposure and measures for the protection of the general public.
This Standard supersedes the 2002 Radiation Protection Standard for Maximum Exposure Levels to Radiofrequency Fields — 3 kHz to 300 GHz (Radiation Protection Series No. 3). This Standard is based on the
2020 guidelines of the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) for RF electromagnetic fields.
Download the New Standard for Radiofrequency by ARPANSA |